tumours of lowmalignant potential and low- and high-grade
papillary UC), flat lesions (carcinoma
in situ
[CIS]), and
invasive carcinoma. As in bladder tumours, nonurothelial
differentiation (i.e., histologic variants) confers an adverse
risk factor.
3.2.2.
Tumour node metastasis staging
The tumour, node, metastasis (TNM) classification is
shown in
Table 1 [18]. The regional lymph nodes are the
hilar and retroperitoneal nodes, and for the mid and distal
ureter, the intrapelvine nodes. Laterality does not affect N
classification.
Renal pelvic pT3 subclassification may discriminate
between microscopic infiltration of the renal parenchyma
(pT3a) and macroscopic infiltration or invasion of peripelvic
adipose tissue (pT3b)
[16,19,20] .pT3b UTUC has a higher
risk of disease recurrence after RNU
[16,19].
3.2.3.
Tumour grade
Until 2004, the 1973 World Health Organisation (WHO)
classification was used for tumour grading and distin-
guished grades G1
–
G3
[1,21]. The 2004 WHO classification
considers histological data to distinguish between nonin-
vasive tumours: papillary urothelial neoplasia of low
malignant potential, and low- and high-grade carcinomas
(low grade versus high grade). The current guidelines are
based on the 2004 WHO classifications
[22].
3.3.
Diagnosis
3.3.1.
Symptoms
The diagnosis of UTUC may be incidental or related to the
evaluation of symptoms that are generally limited
[1]. The
[(Fig._1)TD$FIG]
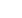
Fig. 1
–
Selection of patients with UTUC for hereditary screening during the first medical interview.
HNPCC = hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal carcinoma; UTUC = upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma.
Table 1
–
TNM classification 2017 for upper tract urothelial
carcinoma
[18]T
—
primary tumour
TX Primary tumour cannot be assessed
T0
No evidence of primary tumour
Ta Noninvasive papillary carcinoma
Tis Carcinoma
in situ
T1
Tumour invades subepithelial connective tissue
T2
Tumour invades muscularis
T3
Tumour invades beyond muscularis into peripelvic fat or renal
parenchyma (renal pelvis)
Tumour invades beyond muscularis into periureteric fat (ureter)
T4
Tumour invades adjacent organs or through the kidney into
perinephric fat
N
—
regional lymph nodes
NX Regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed
N0
No regional lymph node metastasis
N1
Metastasis in a single lymph node 2 cm in the greatest dimension
N2
Metastasis in a single lymph node
>
2 cm, or multiple lymph nodes
M
—
distant metastasis
M0 No distant metastasis
M1 Distant metastasis
TNM = tumour, node, metastasis (classi
fi
cation).
E U R O P E A N U R O L O GY 7 3 ( 2 0 18 ) 111
–
1 2 2
113